Table of Contents
- How Capsaicin Interacts with Sensory Receptors to Trigger Pain
- The Biological Response Behind Eye and Skin Irritation
- Short and Long Term Effects of Pepper Spray Exposure
- Best Practices for Treatment and Minimizing Discomfort After Exposure
- Final Thoughts
How Capsaicin Interacts with Sensory Receptors to Trigger Pain
When capsaicin, the active component in pepper spray, comes into contact with our skin or mucous membranes, it binds to a specific protein known as the TRPV1 receptor. This receptor is typically responsible for detecting heat and physical abrasion, playing a crucial role in our body’s ability to sense pain. Capsaicin essentially tricks these receptors into thinking they’re exposed to extreme heat, even though no actual thermal damage is occurring. This binding triggers an influx of calcium and sodium ions into nerve cells, which sends a powerful pain signal to the brain, resulting in the characteristic burning sensation.
The activation of TRPV1 receptors doesn’t just cause a sharp pain-it also starts a cascade of physiological responses designed to protect the body from harm. This includes:
- Release of neuropeptides: Chemicals like substance P cause inflammation and swelling, amplifying the pain and irritation.
- Activation of nearby sensory neurons: Leading to increased sensitivity and the sensation of burning or itching.
- Reflexive responses: Such as tearing, coughing, or sneezing, which serve to expel the irritant.
Understanding this mechanism highlights why pepper spray is so effective at incapacitating a target temporarily without causing lasting physical damage, relying purely on the nervous system’s pain pathways.
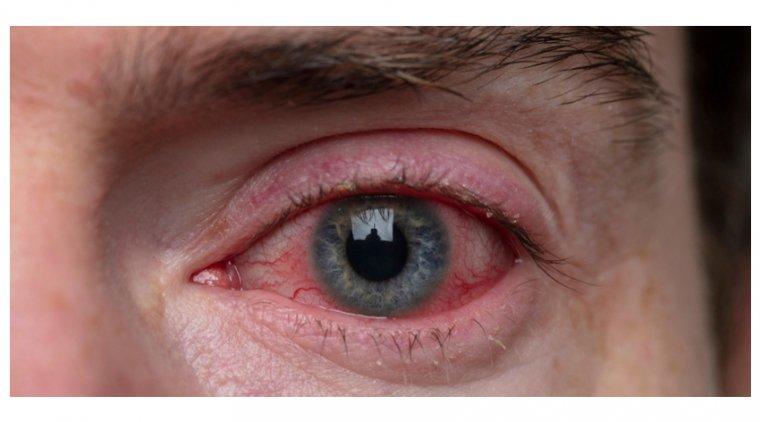
The Biological Response Behind Eye and Skin Irritation
Upon exposure to pepper spray, the active compound capsaicin binds to a receptor called TRPV1, which is present on sensory nerve endings in both the eyes and skin. This receptor is responsible for detecting heat and physical abrasion, so when capsaicin activates it, the brain interprets the sensation as intense burning or heat. This biological mechanism triggers a cascade of responses, including the release of neuropeptides like substance P, which further amplifies the pain signals and induces inflammation. The immediate consequence is a sharp, burning sensation accompanied by redness, swelling, and excessive tearing in the eyes-all defensive reactions aimed at flushing out the irritant and protecting delicate tissues.
Additionally, the irritation prompts the body’s immune system to react swiftly. White blood cells rush to the affected areas, triggering the release of histamines and other inflammatory mediators. These substances increase blood flow and cause capillaries to dilate, intensifying redness and swelling. On the skin, this engenders a painful stinging sensation and sometimes itching. Key factors involved include:
- Neurogenic inflammation: nerve-induced release of pro-inflammatory agents.
- Mucous membrane response: heightened tear and mucus production to wash away irritants.
- Vascular dilation: increased blood flow that contributes to redness and swelling.
Short and Long Term Effects of Pepper Spray Exposure
The immediate aftermath of pepper spray exposure typically involves intense irritation of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract due to the compound capsaicin, the active ingredient responsible for its burning sensation. Short-term effects often include:
- Severe eye redness and tearing
- Burning sensation on the skin
- Coughing, difficulty breathing, and nasal irritation
- Temporary blindness or impaired vision
However, exposure can sometimes trigger long-term effects in sensitive individuals or with repeated contact. These may include:
- Persistent respiratory issues such as asthma exacerbation or bronchitis
- Chronic skin irritation or dermatitis in areas frequently exposed
- Potential scarring from prolonged ocular damage
Best Practices for Treatment and Minimizing Discomfort After Exposure
Immediately after exposure, the foremost priority is to remove irritants to prevent further discomfort. Flush the affected area gently with copious amounts of cool water-avoid using hot water or rubbing the skin, as this can exacerbate the irritation. Eyewash stations or specialized saline solutions are ideal if available, especially for ocular exposure. Avoid touching the face or eyes with contaminated hands, and if possible, remove any clothing that may have trapped residual spray. Rinsing should continue for at least 15 minutes to dilute and wash away capsaicinoids, the active irritants in pepper spray.
Once initial decontamination is underway, focus shifts to comfort and symptom management. Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can soothe burning eyes, while cool compresses applied gently to affected skin help reduce inflammation and redness. It’s important to refrain from using oils, creams, or abrasive scrubs which can trap irritants deeper into the skin or eyes. If symptoms persist beyond an hour or worsen, seek medical attention promptly. Recognizing the limits of home care and ensuring professional evaluation will minimize complications and speed recovery.
- Flush eyes and skin with plenty of water or saline solution.
- Avoid rubbing affected areas to prevent additional irritation.
- Use cool compresses to reduce inflammation.
- Remove contaminated clothing promptly and safely.
- Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms escalate or persist.
Final Thoughts
In understanding why pepper spray causes such intense irritation, we uncover the powerful chemistry behind its effects on the human body. This knowledge not only highlights the effectiveness of pepper spray as a self-defense tool but also underscores the importance of using it responsibly and with caution. By appreciating the science, we can better respect both its potency and the reactions it triggers-reminding us that, while it’s a non-lethal deterrent, it’s anything but gentle. Stay informed, stay safe, and approach pepper spray with the seriousness it demands.Check Our Other Blogs
- StunGun – Your Trusted Source for Stun Guns, Laws, and Self-Defense Tips
- PepperSprayLaws – Your Trusted Resource for Pepper Spray Information
- StunGunLaws – Your Trusted Guide to Stun Gun Legality and Safety