Table of Contents
- Understanding the Prevalence of Allergic Reactions to Pepper Spray
- Recognizing Symptoms and Differentiating from Typical Irritant Effects
- Factors That Increase the Risk of Allergic Responses to Pepper Spray
- Effective First Aid and Medical Recommendations for Allergic Reactions
- The Conclusion
Understanding the Prevalence of Allergic Reactions to Pepper Spray
While pepper spray is widely recognized as an effective self-defense tool, allergic reactions to its active compounds are relatively uncommon but not impossible. The primary irritant in pepper spray is capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, which triggers an inflammatory response in most individuals. However, sensitivity varies, and a small subset of people may experience heightened or prolonged symptoms due to an allergic reaction rather than just irritation. These responses can range from mild skin rashes to more severe respiratory distress in rare cases. It’s essential to differentiate between normal irritation and an allergic response, as the latter may require medical intervention.
Factors influencing susceptibility include:
- Pre-existing allergies: Individuals with hay fever, asthma, or other environmental allergies might be more prone to exacerbated symptoms.
- Skin sensitivity: Those with eczema or other dermatological conditions could experience more intense reactions.
- Repeated exposure: Frequent exposure may increase the likelihood of sensitization and allergic reactions over time.
Understanding these risk factors can help users take precautions and seek appropriate care if adverse effects occur.
Recognizing Symptoms and Differentiating from Typical Irritant Effects
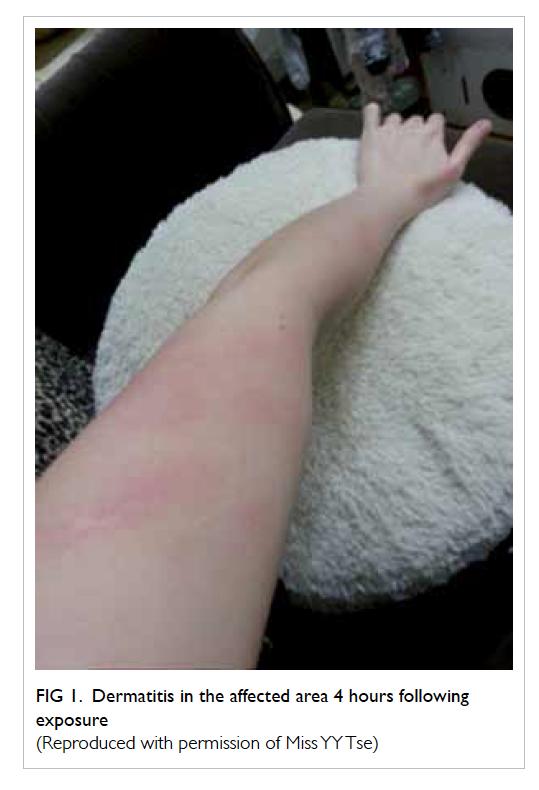
When exposed to pepper spray, most individuals experience immediate irritation characterized by burning sensations in the eyes, nose, throat, and skin. However, distinguishing between typical irritant effects and allergic reactions is crucial for timely and effective care. Common symptoms of a standard irritant response include intense eye redness, tearing, coughing, and temporary difficulty breathing-all generally resolving within minutes to an hour. In contrast, allergic reactions may manifest with additional signs such as persistent swelling, hives, severe itching, or the development of a rash that extends beyond the direct exposure area. These symptoms often indicate the body’s immune system reacting abnormally to compounds in the spray, requiring medical attention.
Key signs to watch for include:
- Swelling of lips, tongue, or throat, potentially leading to breathing difficulties
- Widespread rash or hives lasting more than a few hours
- Severe skin itching or blistering beyond normal irritation
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing that does not improve after initial exposure
Recognizing these distinctive symptoms early ensures that individuals seek prompt medical evaluation, rather than dismissing the reaction as typical pepper spray irritation. Understanding these nuanced differences can help both users and responders manage exposure incidents with greater confidence and safety.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Allergic Responses to Pepper Spray
Several variables can amplify the likelihood of experiencing an allergic reaction to pepper spray, with individual sensitivity playing a pivotal role. People who have a history of allergies, particularly those with respiratory or skin allergies, may find themselves more susceptible. Additionally, repeated exposure to capsaicinoids, the active compounds in pepper spray, can sometimes sensitize the immune system, increasing the chance of an exaggerated response over time. Environmental factors, such as pre-existing asthma or eczema, can also intensify symptoms, making what might typically be a brief irritation turn into a prolonged allergic ordeal.
Other risk factors to consider include:
- Use of medications that alter immune responses, such as immunosuppressants
- Exposure to high concentrations or prolonged exposure to pepper spray
- Underlying chronic respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Skin conditions that compromise the natural barrier, increasing allergen absorption
- Age extremes-young children and the elderly might be more vulnerable
Effective First Aid and Medical Recommendations for Allergic Reactions
When confronted with an allergic reaction from pepper spray exposure, swift and calm action can significantly alleviate symptoms. Begin by moving the affected individual to fresh air to minimize further inhalation of irritants. Rinse the exposed skin and eyes thoroughly with cold water for at least 15 minutes, avoiding any rubbing that can worsen irritation. Removing contaminated clothing is also crucial to prevent prolonged contact. Over-the-counter antihistamines may help reduce itching and swelling, but monitor the person closely for escalating symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or persistent chest tightness.
Seek immediate emergency medical attention if you notice any of the following signs:
- Severe respiratory distress, wheezing, or throat tightness
- Rapid swelling of lips, tongue, or face
- Loss of consciousness or extreme dizziness
- Persistent chest pain or severe headache
Medical professionals may administer epinephrine or corticosteroids to counteract severe allergic reactions and prevent anaphylaxis. Always inform responders about the pepper spray exposure to ensure appropriate, targeted treatment. Having a well-stocked first aid kit that includes basic supplies for allergic reactions can be a lifesaver in such unexpected scenarios.
The Conclusion
In conclusion, while allergic reactions to pepper spray are relatively uncommon, they remain a possibility that users and responders should be aware of. Understanding how your body might respond and knowing the appropriate first aid measures can make a significant difference in managing any adverse effects. Staying informed and prepared ensures that pepper spray remains a safe and effective tool for personal protection. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect an allergic reaction or experience prolonged symptoms after exposure.Check Our Other Blogs
- StunGun – Your Trusted Source for Stun Guns, Laws, and Self-Defense Tips
- PepperSprayLaws – Your Trusted Resource for Pepper Spray Information
- StunGunLaws – Your Trusted Guide to Stun Gun Legality and Safety